In an uncertain world, the specter of mortality is a reality that touches every human life. While death can occur due to a multitude of causes, it is vital to understand and address the primary factors that lead to human fatalities on a global scale.
The data is drawn from reputable international bodies such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the World Health Federation (WHF), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Understanding these causes is an essential step towards improving global health and reducing mortality rates. This exploration delves into the top 15 common causes of death in humans worldwide.
Causes of Death in Humans around the World:
15. Suicide:

Suicide represents a poignant worldwide issue that, until 2023, has resulted in the loss of many lives.
This complex problem is affected by a myriad of elements, encompassing mental health, societal pressures, and economic circumstances.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nearly 800,000 individuals succumb to suicide annually, marking it as a substantial source of preventable fatalities.
Mitigating suicide rates demands a collective commitment to bolster mental health assistance, promote awareness, and dismantle the stigma associated with mental health challenges.
14. Hypertension:
Chronic Liver Disease, often caused by factors like viral hepatitis, excessive alcohol consumption, or fatty liver disease, can lead to severe health complications and, in some cases, death.
Over time, the liver becomes scarred and less functional, increasing the risk of liver failure, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Sadly, chronic liver disease can ultimately result in death if not managed effectively. Early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, and medical treatment can help slow its progression and improve the quality of life for those affected.
However, for some individuals, especially in advanced stages of the disease, liver transplantation may be the only option to prevent a fatal outcome.
13. HIV/AIDS:
HIV/AIDS has claimed millions of lives worldwide. The virus weakens the immune system, making individuals susceptible to various infections and diseases.
Without proper medical care and treatment, HIV can progress to AIDS, a condition that often leads to severe illness and, ultimately, death.
However, advancements in antiretroviral therapy (ART) have greatly improved the outlook for people with HIV, allowing many to manage the virus and lead longer, healthier lives.
While there is still no cure, increased awareness, prevention efforts, and access to treatment have reduced HIV/AIDS-related deaths in recent years.
12. Malnutrition:

Malnutrition is a condition where the body doesn’t get the necessary nutrients it needs for health and growth. Severe malnutrition can lead to death, particularly in vulnerable populations like children and the elderly.
It weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and other health issues.
Addressing malnutrition involves improving access to nutritious food, clean water, and healthcare, especially in impoverished regions, to prevent unnecessary deaths due to this condition.
11. Tuberculosis:

Tuberculosis, or TB, is a lung-focused bacterial infection that, when left untreated, can turn life-threatening.
This contagious disease is transmitted through the air when an infected individual coughs or sneezes, resulting in symptoms like persistent coughing, fever, and weight loss.
Fortunately, TB is treatable with antibiotics, but without timely diagnosis and proper treatment, it can progress to severe illness and fatality.
To decrease the mortality rates associated with TB, the implementation of robust TB control initiatives and early detection mechanisms is imperative.
10. Diarrheal Diseases:
Diarrheal illnesses pose a significant risk to lives, especially among children and susceptible communities. They result in frequent, liquid bowel movements, which can lead to severe dehydration and nutrient depletion.
The transmission of these diseases is often linked to impure water sources and inadequate sanitation.
However, many fatalities due to diarrhea can be averted through timely rehydration treatment and appropriate healthcare.
Enhancing public health measures for sanitation and ensuring access to clean water sources is essential for reducing the mortality associated with diarrheal diseases.
9. Nephritis:
Nephritis can lead to severe health complications and, in some cases, result in death. This condition, characterized by inflammation of the nephrons in the kidneys, can cause kidney damage and impair their function.
Timely medical intervention and management are crucial in preventing fatal outcomes associated with nephritis. Monitoring and treatment focused on preserving kidney health are vital in reducing the risk of death due to this condition.
8. Influenza and Pneumonia:
Influenza and pneumonia are respiratory infections that can lead to serious health consequences. Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is caused by influenza viruses and can result in symptoms such as fever, cough, and body aches.
Pneumonia, on the other hand, is an inflammatory lung condition often triggered by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Both conditions can be life-threatening, especially for the very young, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Vaccination against the flu and timely medical treatment for pneumonia are essential in reducing the risk of severe illness and death associated with these infections.
7. Diabetes:
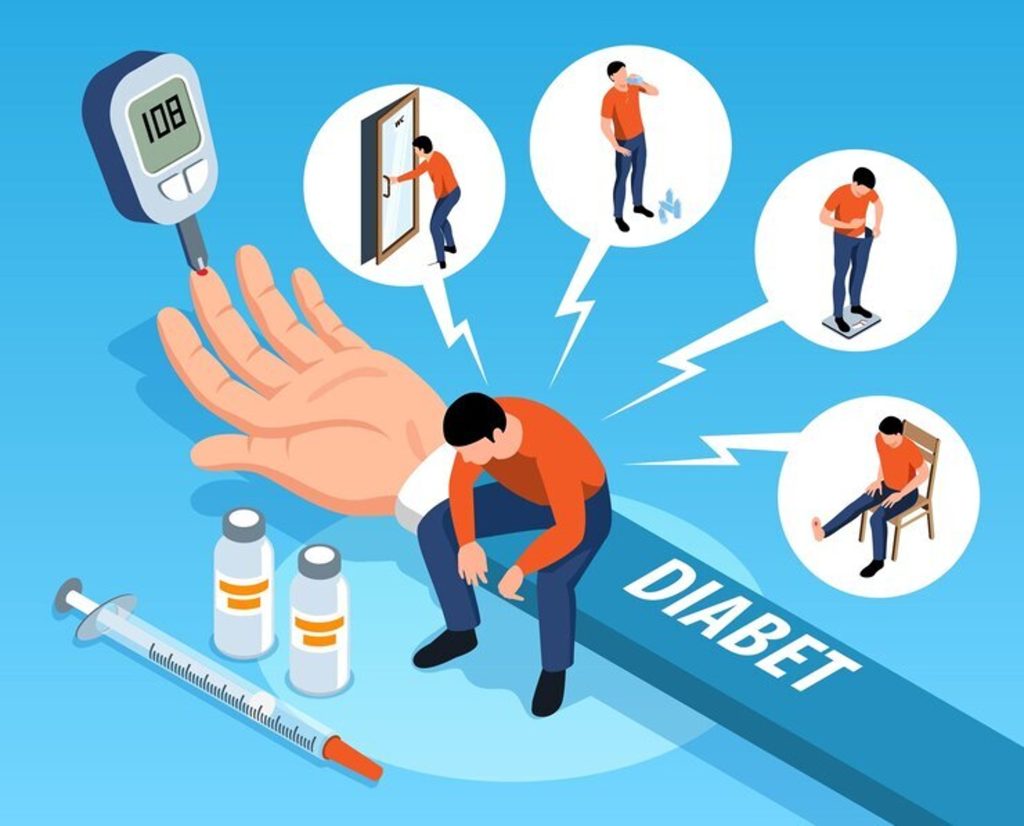

The impact of diabetes-related deaths extends worldwide, making it a significant global health concern.
Millions of individuals across the globe are affected by this condition, and it stands as one of the primary contributors to mortality rates.
Uncontrolled diabetes gives rise to severe complications, including heart disease, stroke, renal issues, and nerve damage, ultimately leading to premature fatalities.
This emphasizes the urgent need to increase awareness, encourage early diagnosis, and implement effective global-scale diabetes management strategies to mitigate its profound impact on mortality rates.
6. COPD:
COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, encompasses a collection of progressive lung ailments, with emphysema and chronic bronchitis being among the most prevalent.
Often, individuals with COPD suffer from both conditions concurrently. Emphysema impairs the air sacs in the lungs, obstructing outward airflow, while bronchitis triggers inflammation and constricts the bronchial tubes, leading to mucus accumulation.
Prompt treatment for COPD is imperative, as delaying it can accelerate disease progression, give rise to heart issues, and increase vulnerability to respiratory infections.
Shockingly, this perilous ailment accounts for 2.75 million fatalities globally.
5. Lower respiratory tract infection:
Another prevalent contributor to global mortality is lower respiratory tract infections. These infections occur when the lungs become afflicted, typically by viruses or other microorganisms.
Lower respiratory tract infections are highly transmissible, spreading from person to person through sneezing and coughing.
Failing to address an untreated lower respiratory tract infection can culminate in a distressing fatality. Generally, these infections persist for a span of three to fourteen days.
If symptoms persist beyond the two-week mark, it may signify a more serious and potentially hazardous condition.
4. Stroke:

Another prevalent and perilous affliction in the human body is a stroke. A stroke occurs when the normal blood supply to the brain is disrupted, and it can strike at any time, even during sleep.
This devastating condition stands as a leading cause of disability among adults, with over 795,000 individuals succumbing to its effects.
When brain cells perish, so do vital cognitive functions, often resulting in permanent disabilities that encompass language, mood, vision, and movement.
The dire consequence of a stroke is death, which transpires when the brain remains deprived of oxygen and blood for an extended duration.
It’s noteworthy that an estimated 14 percent of stroke cases culminate in fatalities occurring during sleep.
3. kidney disease:
Kidney disease deaths are a global concern, largely stemming from chronic kidney diseases and, in severe cases, kidney failure.
Healthy kidney function is vital for waste removal and overall health. When their function declines, it results in serious health issues.
Neglected kidney problems may lead to death, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis, proper care, and lifestyle changes to reduce mortality risk.
Kidney failure, a prominent cause of death, can progress over months to years, drastically shortening life expectancy.
Damaged kidneys cannot effectively filter the blood, causing toxin buildup, potentially proving fatal. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) has various stages, with Stage 5 signifying complete kidney failure.
High blood sugar, hypertension, or low blood pressure can harm the kidneys, disturbing necessary blood flow balance and potentially causing death.
Also Read:
1. Benefits Of Asphalt Roofing
2. Most Popular American Shoe Brands
2. Cancer:
Cancer is a global crisis, driving millions of deaths yearly. Uncontrolled cell growth within the body leads to severe complications and fatalities if left untreated.
Early detection, effective treatments, and ongoing research are vital to reduce its impact. Globally, cancer ranks as the second leading cause of death, often linked to age, smoking, pollutants, and genetics.
Lung cancer is a common fatality. Though cancer lacks specific early symptoms, extensive research aims to identify and prevent it at an early stage. Each year, 9.5 million lives are claimed by cancer.
1. Heart Disease:
Heart disease is a global concern, encompassing various heart-related conditions, making it a leading cause of death.
Conditions like coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and heart failure contribute to severe complications and fatalities if not promptly addressed.
Early detection, lifestyle changes, and medical interventions are vital for reducing the impact of heart disease.
It’s the primary cause of death worldwide, particularly affecting men, with plaque buildup in arteries causing circulatory issues leading to angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
A healthy diet and regular exercise mitigate the risk. Recognizing symptoms is crucial for early assessment.